Appearance
Behavioral Patterns
Last Updated: Dec 7, 2024
Behavioral patterns focus on communication and responsibilities between objects, making interactions more flexible and organized.
WARNING
I am only listing the ones that I've been dealing with or interact with a couple of times 😃
TL;DR
Observer: Notifies multiple objects of state changes in a central object, great for event-driven systems.State: Allows an object’s behavior to change based on its internal state.Template Method: Defines a skeleton of an algorithm, allowing subclasses to customize parts of it.
Observer Pattern
Definition
The Observer Pattern establishes a one-to-many dependency between objects, so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
Subjectis an object that maintains a list of observers and notifies them of state changes.Observersare objects that subscribe to the subject to receive updates.
Flow
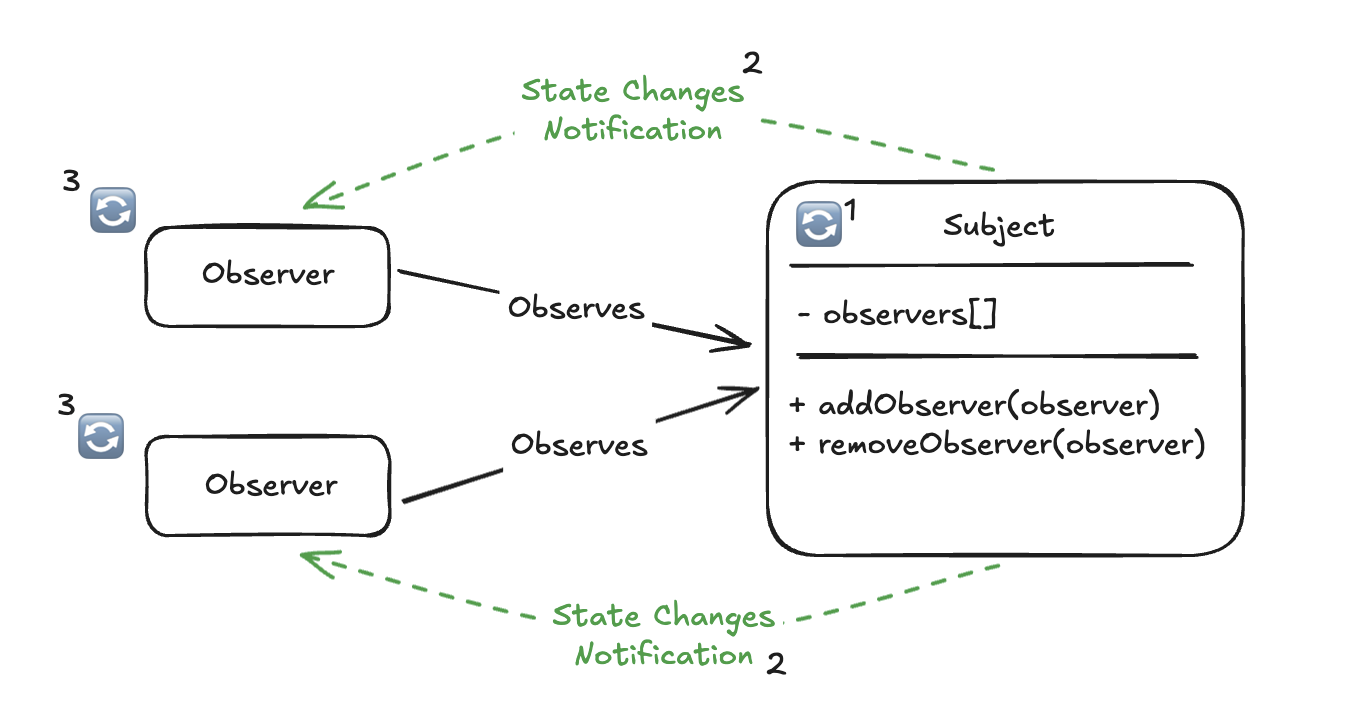
State Change: TheSubject's state changes (e.g., data is updated).Notification: TheSubjectnotifies all registeredObserversof the change.Observer Reaction: EachObserverreacts to the notification, which may involve updating the UI or performing some other action.
State Pattern
Definition
The State Pattern establishes a one-to-many dependency between objects, so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
Subjectis an object that maintains a list of observers and notifies them of state changes.Observersare objects that subscribe to the subject to receive updates.
Flow
State Change: TheSubject's state changes (e.g., data is updated).Notification: TheSubjectnotifies all registeredObserversof the change.Observer Reaction: EachObserverreacts to the notification, which may involve updating the UI or performing some other action.
Template Method Pattern
Definition
The Template Method Pattern establishes a one-to-many dependency between objects, so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
Subjectis an object that maintains a list of observers and notifies them of state changes.Observersare objects that subscribe to the subject to receive updates.
Flow
State Change: TheSubject's state changes (e.g., data is updated).Notification: TheSubjectnotifies all registeredObserversof the change.Observer Reaction: EachObserverreacts to the notification, which may involve updating the UI or performing some other action.
