Appearance
CD (Continuous Deployment) with GitHub Actions
Last Updated: Dec 7, 2024
Continuous Deployment (CD) automates the deployment of code to a production environment, allowing teams to deliver new features, fixes, and updates to users quickly. This tutorial builds on our CI setup by showing how to automatically deploy code once it has passed the CI checks.
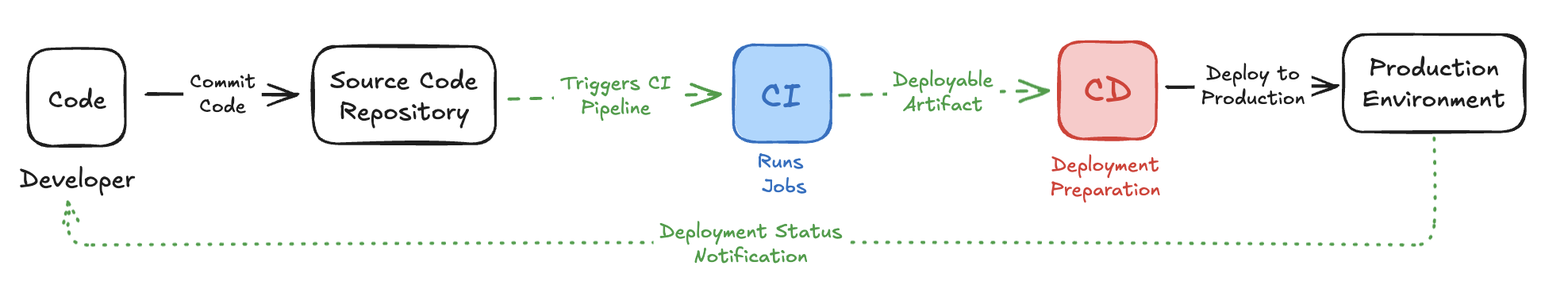
What is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous Deployment deploys code to a live environment after it passes all tests and validation steps. Unlike CI, which only verifies the code, CD makes the verified code available to end-users immediately, providing faster feedback and delivering value continuously.
GitHub Actions
Will we be using GitHub Actions to implement a CI into a Github repository. But first, what is Github Actions?
GitHub Actions is a CI/CD (Continuous Implementation and Continuous Deployment) tool integrated directly into GitHub, allowing developers to automate tasks and workflows around their code. With this tool, you can build, test, and deploy your code automatcally is response to events in the repository, such as pushes, pull requests, etc.
CD Implementation
We will implement our CD pipeline, automatically deploying the code when new changes are merged into the main branch. Depending on your tech stack, you may deploy to various services like AWS, Heroku, Firebase, or others. In this example, we’ll cover a deployment to GitHub Pages, a common choice for static websites.
INFO
In this note, we will follow the example of implementing a CD into GitHub Pages with a Vitepress site. This example applies for any kind of CD! You must adapt to your needs.
Creating the CD Workflow File
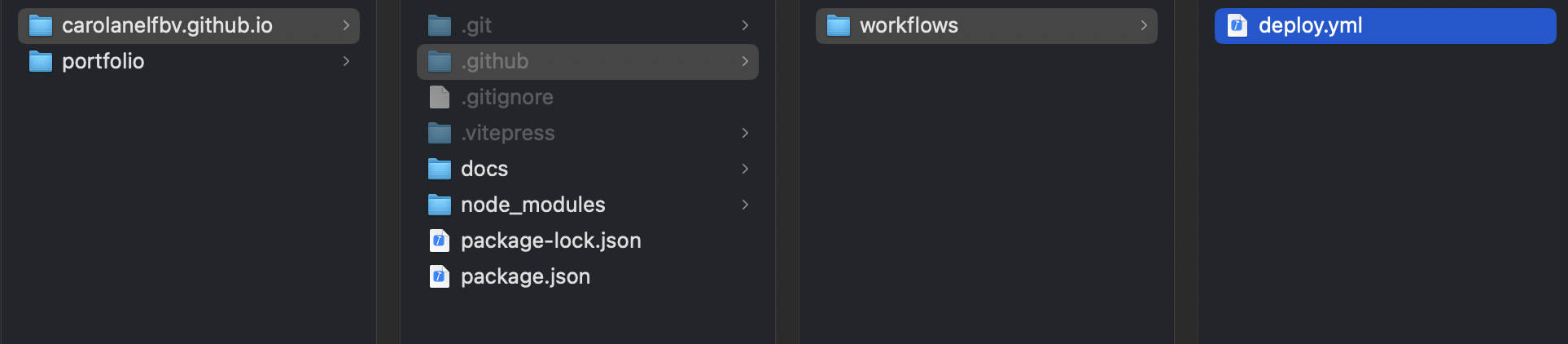
First, create a new YAML file in your .github/workflows directory. This file will define the steps needed to deploy the application to GitHub Pages.
WARNING
When developing a Vitepress site, the deploy.yml file is automatically generated. So please, check if there's already a folder with a deploy yaml file. If not, create it.
yaml
name: Deploy VitePress site to Pages
on:
# Runs on pushes targeting the `main` branch. Change this to `master` if you're
# using the `master` branch as the default branch.
push:
branches: [main]
# Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
workflow_dispatch:
# Sets permissions of the GITHUB_TOKEN to allow deployment to GitHub Pages
permissions:
contents: read
pages: write
id-token: write
# Allow only one concurrent deployment, skipping runs queued between the run in-progress and latest queued.
# However, do NOT cancel in-progress runs as we want to allow these production deployments to complete.
concurrency:
group: pages
cancel-in-progress: falseBreakdown of the CD Workflow
Configuration
- The
nameparameter corresponds to the name of your CD. - Triggers
onDefines when the CI is triggered.push: We set this to trigger onpushevents to themainbranch, so each merge will automatically trigger a deployment.
- Permissions
- Grants
pages: writepermissions to theGITHUB_TOKENfor deployment to GitHub Pages.
- Grants
- Concurrency
- Configures the workflow to allow only one deployment at a time, ensuring no overlapping deployments.
Jobs: Build and Deploy
yaml
jobs:
# Build job
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0 # Not needed if lastUpdated is not enabled
# - uses: pnpm/action-setup@v3 # Uncomment this block if you're using pnpm
# with:
# version: 9 # Not needed if you've set "packageManager" in package.json
# - uses: oven-sh/setup-bun@v1 # Uncomment this if you're using Bun
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 20
cache: npm # or pnpm / yarn
- name: Setup Pages
uses: actions/configure-pages@v4
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci # or pnpm install / yarn install / bun install
- name: Build with VitePress
run: npm run docs:build # or pnpm docs:build / yarn docs:build / bun run docs:build
- name: Upload artifact
uses: actions/upload-pages-artifact@v3
with:
path: docs/.vitepress/dist- Jobs
jobsDefines a set or tasks executed in the workflow.- Here, the job is named
deploy. runs-onis like an image on docker, it will use the image to emulate a specific environment.
- Here, the job is named
- Steps
stepsare the different milestones it's going to take in order to run the job.- Checkout: Checks out the code to the runner.
- Setup Node: Ensures Node.js is available, and sets it up.
- Install dependencies: Installs all dependencies required by the project.
- Build with VitePress: Runs the build command to compile the site.
- Upload artifact: Uploads the build files to GitHub Pages for deployment.
Deployment Job
yaml
# Deployment job
deploy:
environment:
name: github-pages
url: ${{ steps.deployment.outputs.page_url }}
needs: build
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Deploy
steps:
- name: Deploy to GitHub Pages
id: deployment
uses: actions/deploy-pages@v4- Environment: It specifies the deployment environment as github-pages.
- needs: Ensures the deploy job only runs after a successful build.
- Deploy to GitHub Pages: Uses the deploy-pages action to publish the site.
GitHub Token and Secrets
To secure deployment, we use secrets.GITHUB_TOKENis automatically generated and scoped for each repository. It allows the workflow to interact with GitHub’s APIs and deploy the site. If deploying to a different environment, add relevant secrets in your repository’s Settings > Secrets and variables.
Customizing for Different Platforms
For other platforms:
- Firebase Hosting: Use the
Firebase CLI Actionwithfirebase-tools. - AWS S3 or EC2: Use AWS CLI commands or GitHub Actions for AWS.
- Heroku: Use the
git pushmethod or GitHub’s Heroku Actions.
Conclusion
With Continuous Deployment set up, every code change merged into the main branch will automatically be built and deployed, creating a streamlined, hands-off process from code to production. You can find this example setup and customize it further by visiting the repository.
By completing both CI and CD, you’ve established a full CI/CD pipeline, letting you deliver code changes confidently and efficiently.
